Burma is a country in South Asia and Southeast Asia. It is, bordered by India, Bangladesh, China, Laos and Thailand. The country was colonized by Britain following three Anglo-Burmese Wars (1824–1885). British rule brought social, economic, cultural and administrative changes to the once-feudal society. Since independence in 1948, the country has been in one of the longest running civil wars among the country's myriad ethnic groups that remains unresolved. From 1962 to 2011, the country was under military rule. The State Peace and Development Council was the official name of the military regime of Burma (also known as Myanmar), which seized power in 1988. It rejected the 1990 election results and kept Aung San Suu Kyi under house arrest until her release on 13 November 2010. The council was officially dissolved on 30 March 2011, with the inauguration of the newly elected government, led by its former member and Prime Minister, President Thein Sein.
2011–2012 Burmese political reforms
The 2011-2012 Burmese democratic reforms are a series of political, economic and administrative reforms in Burma undertaken by the military backed Union Solidarity and Development Party (USDP). These reforms include the release of pro-democracy leader Aung San Suu Kyi from house arrest and subsequent dialogues with her, establishment of the National Human Rights Commission, general amnesties of more than 200 political prisoners, institution of new labor laws that allow labour unions and strikes, relaxation of press censorship and regulations of currency practices. Aung San Suu Kyi's party, the National League for Democracy participated in by-elections held on 1 April 2012 after the government abolished laws that led to the NLD's boycott of the 2010 general election. She led the NLD in winning the by-elections in a landslide, winning 41 out of 44 of the contested seats, with Suu Kyi herself winning a seat representing Kawhmu Constituency in the lower house of the Burmese Parliament.
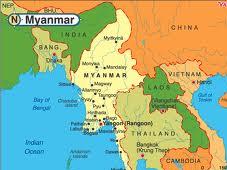
Geography of Burma
It is bordered to the northwest by the Chittagong Division of Bangladesh and the Mizoram, Manipur, Nagaland and Arunachal Pradesh states of India to the northwest. Its north and northeast border straddles the Tibet and Yunnan regions of China for a Sino-Burman border. It is bounded by Laos and Thailand to the southeast. Burma has 1,930 kilometres (1,200 mi) of contiguous coastline along the Bay of Bengal and Andaman Sea to the southwest and the south.
Economy of Burma
The country is one of the poorest nations in Southeast Asia, suffering from decades of stagnation, mismanagement and isolation. The lack of an educated workforce skilled in modern technology contributes to the growing problems of the economy. Under British administration, Burma was the second-wealthiest country in South-East Asia. It had been the world's largest exporter of rice. Burma also had a wealth of natural and labour resources. It produced 75% of the world's teak and had a highly literate population. After a parliamentary government was formed in 1948, Prime Minister U Nu embarked upon a policy of nationalization and the state was declared the owner of all land. The government also tried to implement a poorly considered Eight-Year plan. By the 1950s, rice exports had fallen by two thirds and mineral exports by over 96% (as compared to the pre-World War II period). Plans were partly financed by printing money, which led to inflation. The 1962 coup was followed by an economic scheme called the Burmese Way to Socialism, a plan to nationalise all industries, with the exception of agriculture. The catastrophic program turned Burma into one of the world's most impoverished countries. Burma's admittance to Least Developed Country status by the UN in 1987 highlighted its economic bankruptcy.
Did you know?
1. The national currency of Burma is Kyat.
2. The major agricultural product of Burma is rice which covers about 60% of the country's total cultivated land area.
3. Burma is the world's second largest producer of opium, accounting for 8% of entire world production and is a major source of illegal drugs.
4. 90% of the world's rubies come from Burma, whose red stones are prized for their purity and hue.
5. 89% of the population of Burma embraces Buddhism.
6. The World Health Organization ranked Burma at 190th, the worst performing of all countries.
sources
1. http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Aung_San_Suu_Kyi
2. http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Burma
3. http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/2011%E2%80%932012_Burmese_political_reforms





0 comments: